2012-01-19 [iOS]モーダルViewController
例えば、Twitterアプリケーションの投稿画面の様に、iPhoneではモーダル・ビューがよく利用される。写真撮影で使われるUIImagePickerControllerもモーデル・ビューとして実装されていて、独自のモーダル・ビューを実装する場合の参考になる。
モーダル・ビューの為のUIViewControllerのサブクラスを用意する。 その際、モーダル・ビューの呼び出し元の為のデリゲートを作成する。
@class ModalPaneViewController;
@protocol ModalPaneViewControllerDelegate
- (void)modalPaneViewControllerDidDone:(ModalPaneViewController *)modalPaneViewController;
- (void)modalPaneViewControllerDidCancel:(ModalPaneViewController *)modalPaneViewController;
@end
そして、モーダル・ビューのビュー・コントローラに呼び出し元のデリゲートをプロパティとして追加する。
@interface ModalPaneViewController : UIViewController
@property (nonatomic, weak) id delegate;
- (IBAction)done:(id)sender;
- (IBAction)cancel:(id)sender;
@end
モーダル・ビューで、デリゲートのメソッドを呼んであげると、呼び出し元に制御が戻る。
@implementation ModalPaneViewController
@synthesize delegate = _delegate;
- (IBAction)done:(id)sender
{
if ([self.delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(modalPaneViewControllerDidDone:)]) {
[self.delegate modalPaneViewControllerDidDone:self];
}
}
- (IBAction)cancel:(id)sender
{
if ([self.delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(modalPaneViewControllerDidCancel:)]) {
[self.delegate modalPaneViewControllerDidCancel:self];
}
}
@end
呼び出し元のモーダル・ビューを開くコードは以下のとおり。
- (IBAction)modalPane:(id)sender
{
ModalPaneViewController *viewController = [[ModalPaneViewController alloc]
initWithNibName:@"ModalPaneViewController"
bundle:nil];
viewController.delegate = self;
[self presentModalViewController:viewController animated:YES];
}
呼び出し元でデリゲートのメソッドを実装。その際に、モーダル・ビューを閉じるコードを呼ぶ。
- (void)modalPaneViewControllerDidDone:(ModalPaneViewController *)modalPaneViewController
{
[self dismissModalViewControllerAnimated:YES];
}
- (void)modalPaneViewControllerDidCancel:(ModalPaneViewController *)modalPaneViewController
{
[self dismissModalViewControllerAnimated:YES];
}
呼び出し元のボタンを押下すると、モーダル・ビューが表示され。
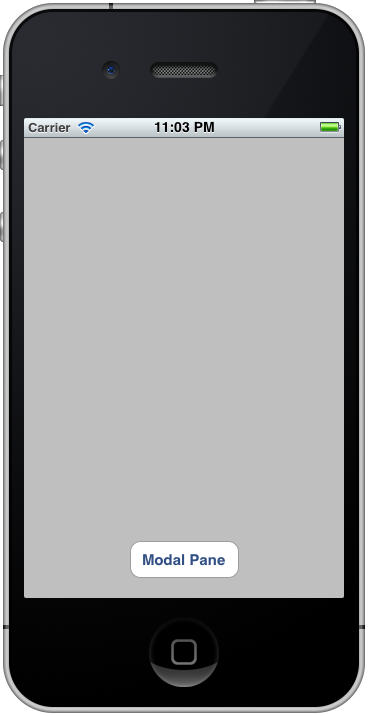
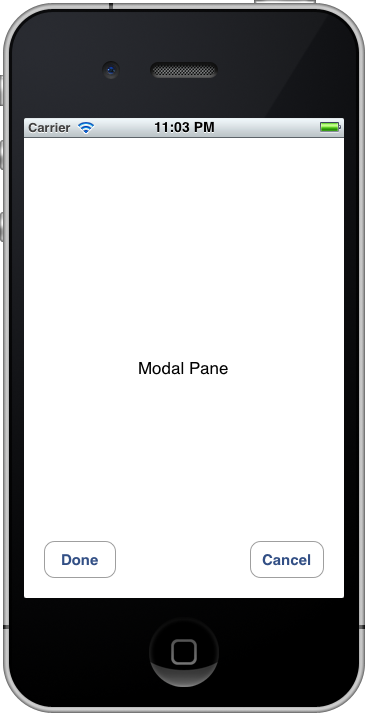
モーダル・ビューのボタンを押下すると、モーダル・ビューは閉じる。



_ eien [delegateメソッドを呼ぶ前に、delegateがそれをサポートしているかどうか確認したほうが安全なコードになり..]
_ m_yukio [確かに、そうですね! 参考にさせていただきます。早速、修正しました。]